
The Death Penalty for Drug Offences: Global Overview 2022
download full reportmain findings
35
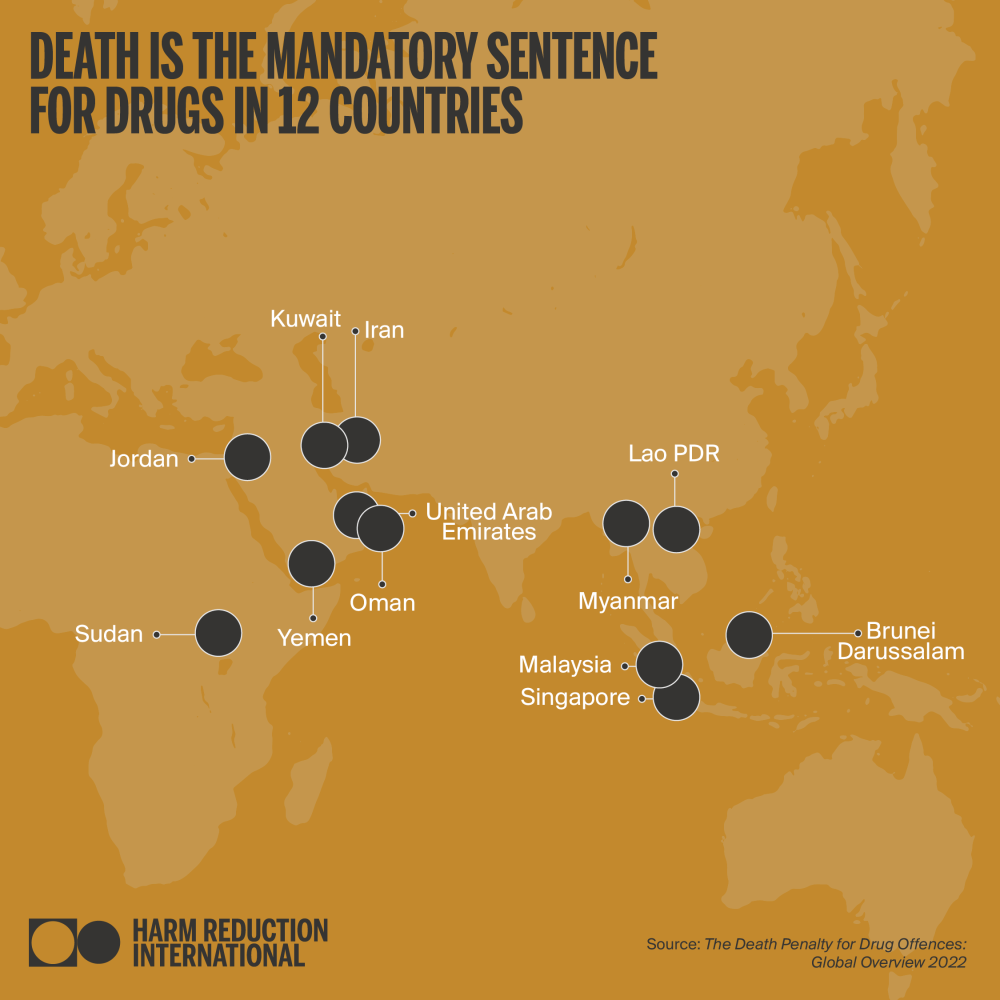
countries still retain the death penalty for drug offences
285+
people executed in 2022
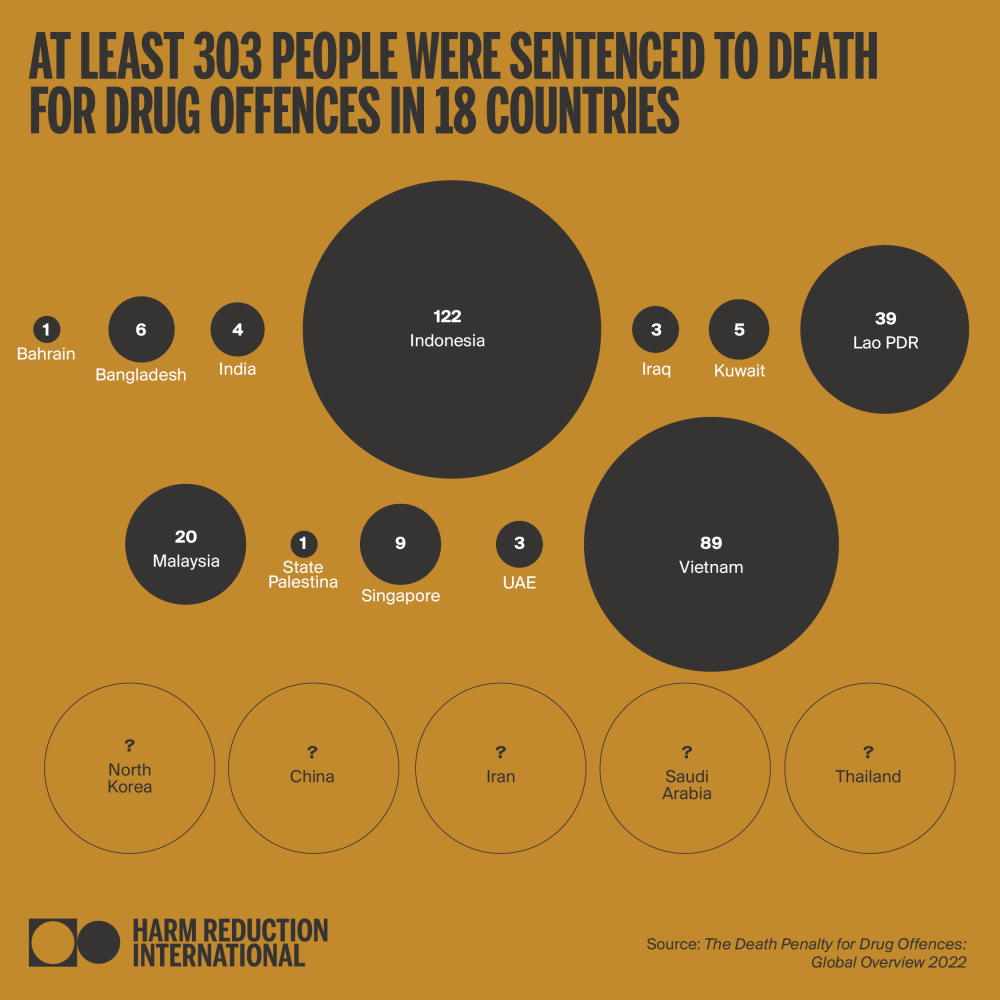
303+
death sentences imposed in 2022
3700+
people on death row for drug offences worldwide
Introduction
Harm Reduction International has monitored the use of the death penalty for drug offences worldwide since our first ground-breaking publication on this issue in 2007. This report, our twelfth on the subject, continues our work of providing regular updates on legislative, policy and practical developments related to the use of capital punishment for drug offences, a practice which is a clear violation of international standards.
Executive Summary
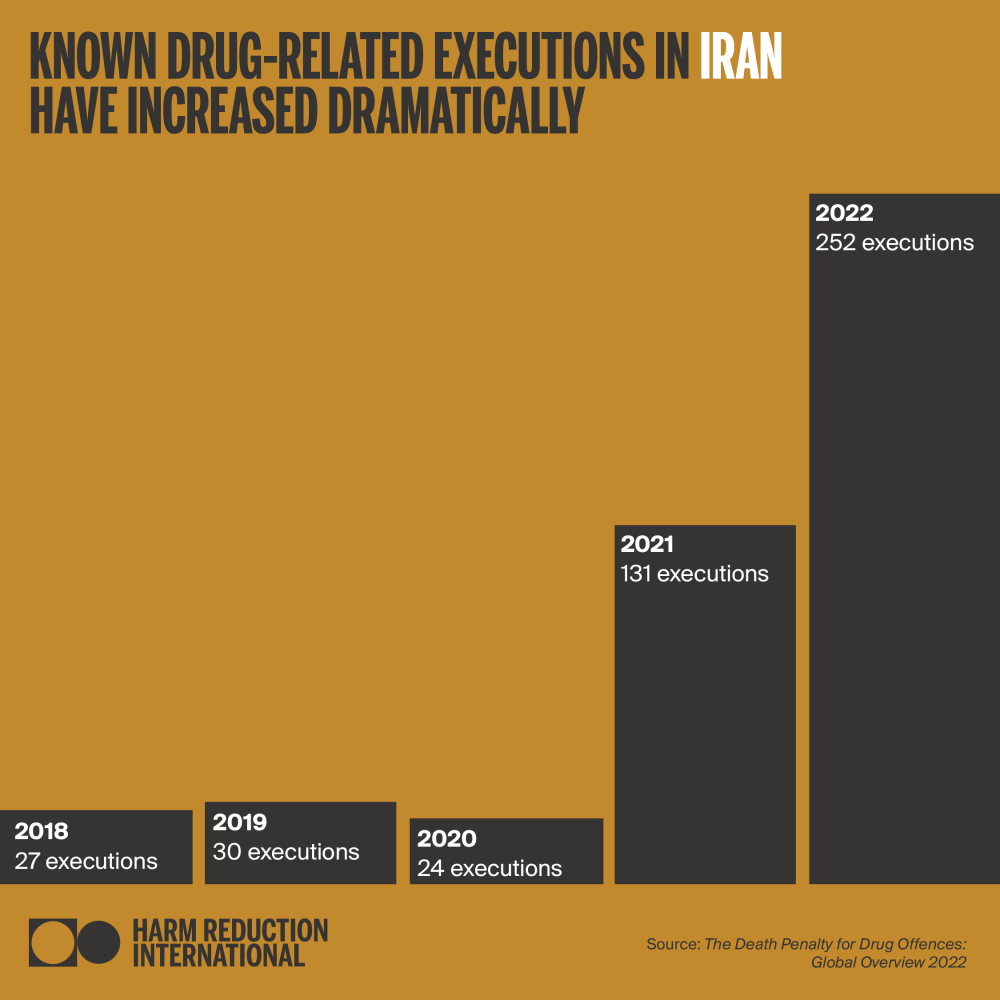
The Global Overview 2021 revealed that 2021 had ended as a year of mixed progress. On one side, the number of countries executing people for drug crimes had reached a decade-low, owing mostly to a halt in drug-related executions in Saudi Arabia and, to some extent, the COVID-19 pandemic. On the other side, a significant increase in confirmed executions had been recorded, largely attributable to a surge in Iran. In the course of 2022, the situation sharply deteriorated.
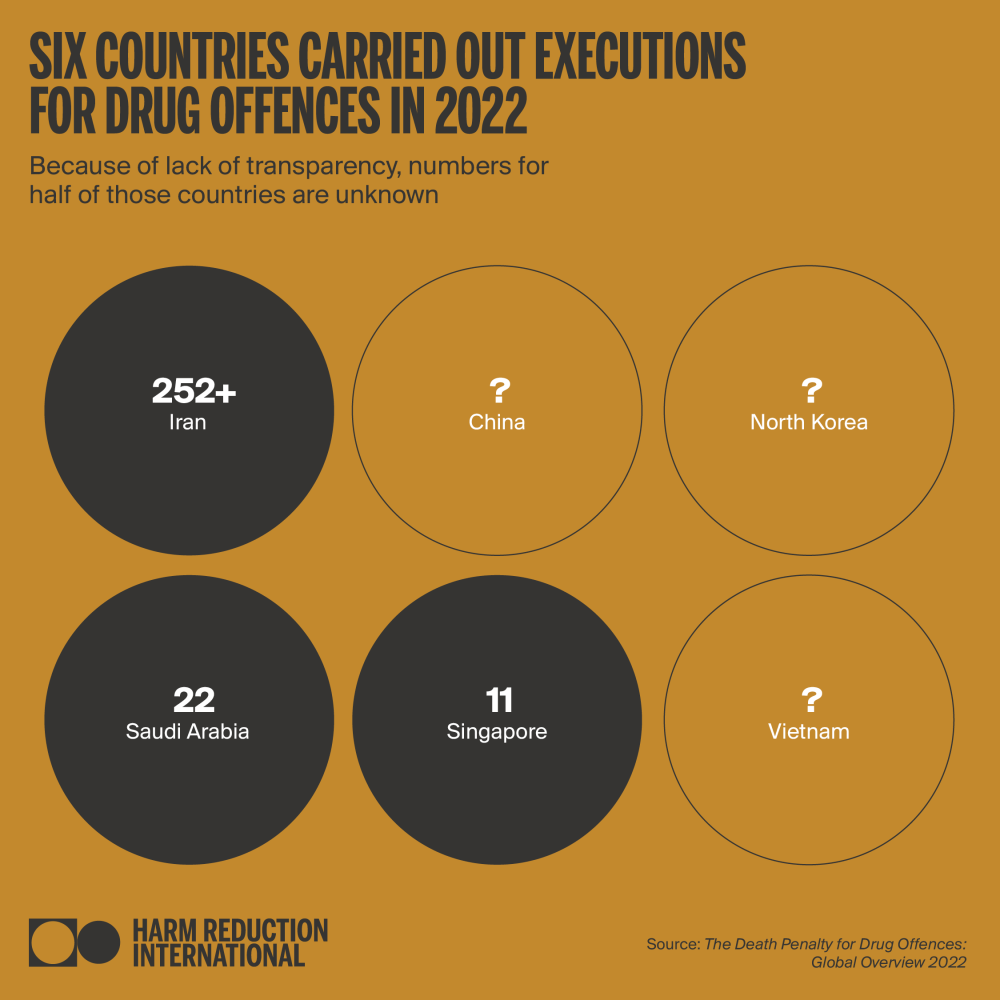
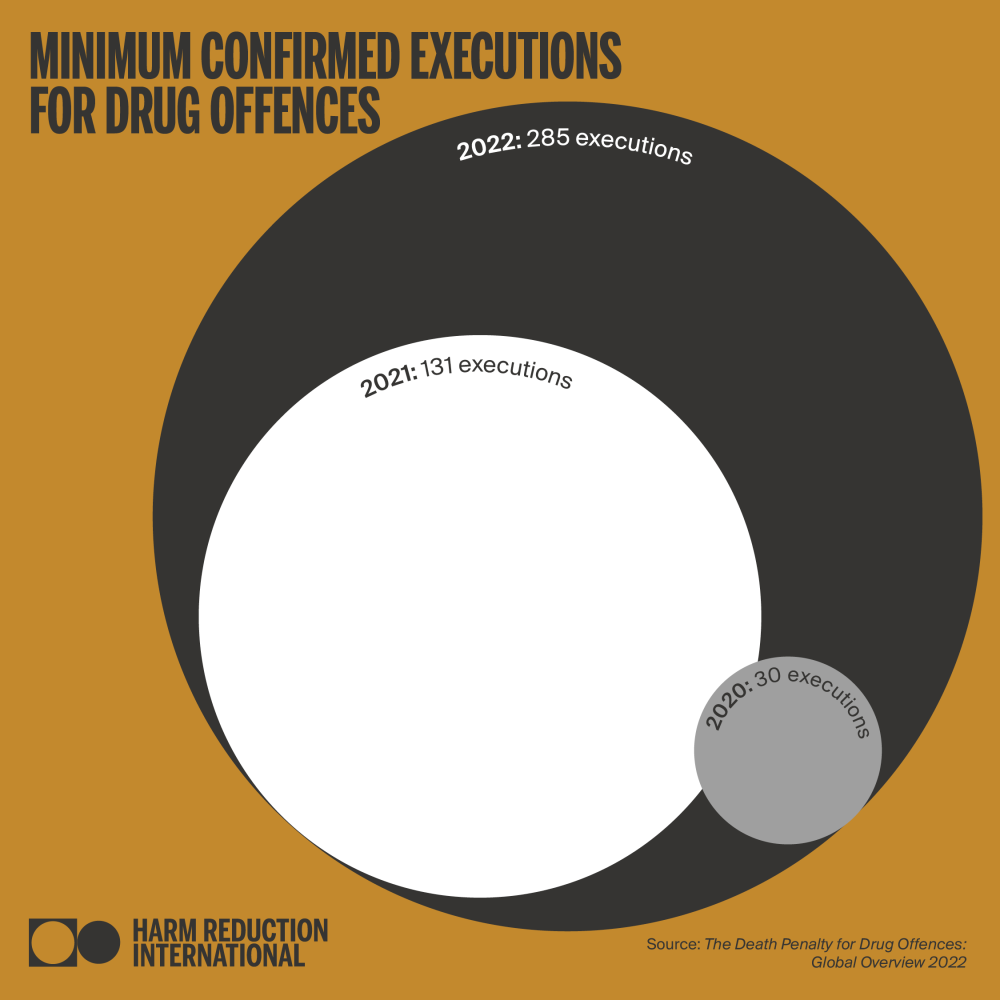
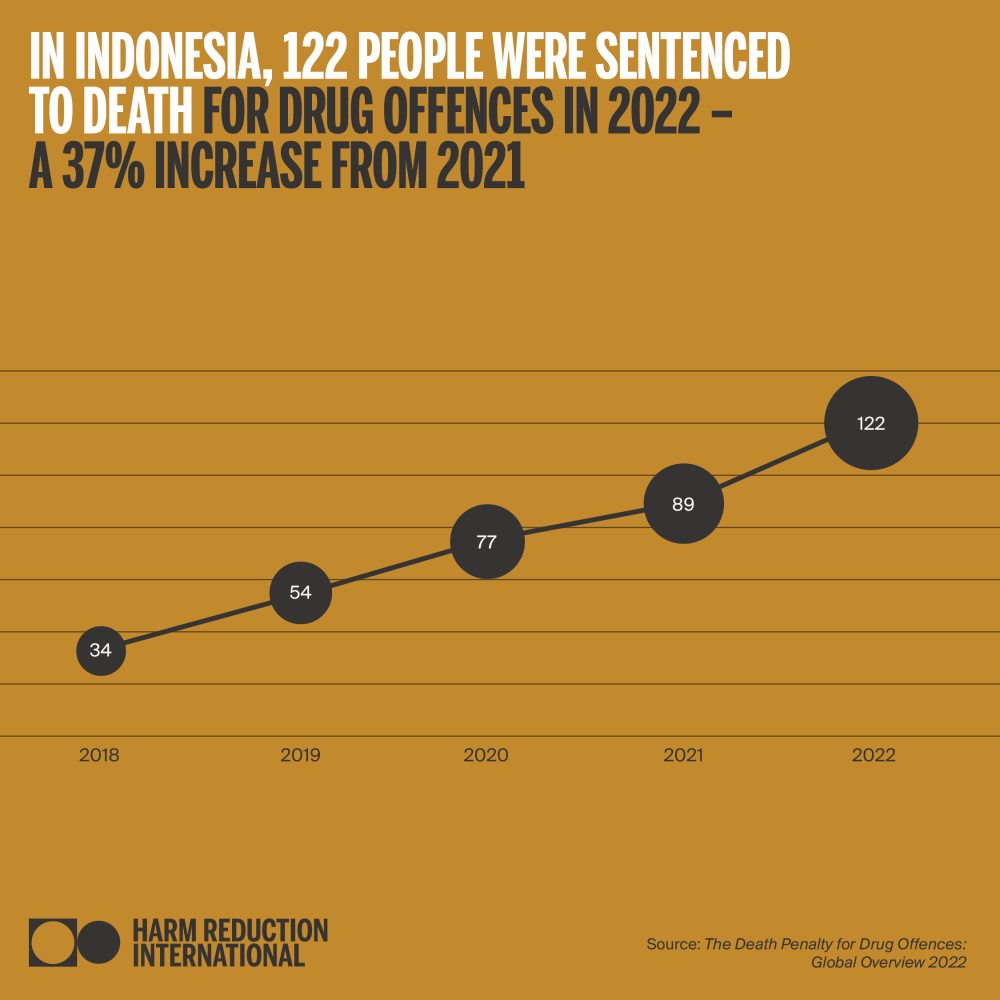
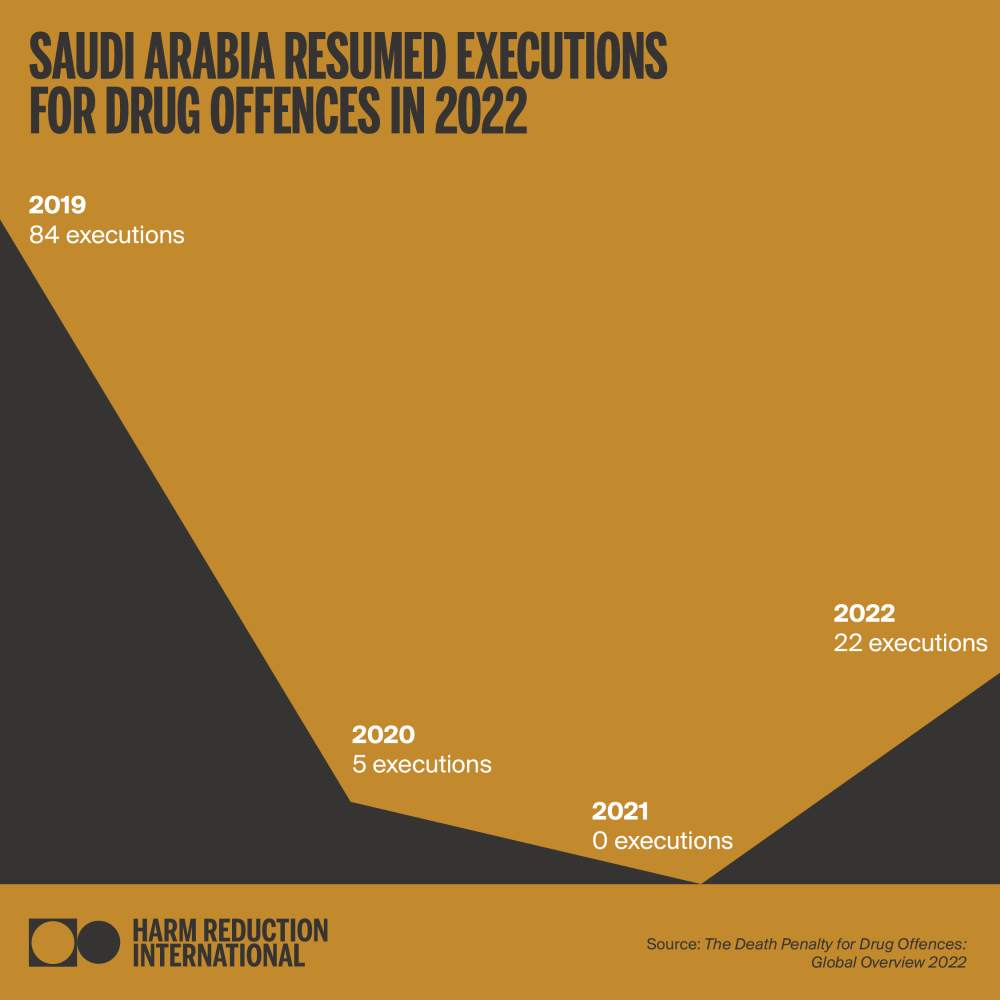
As of December 2022, Harm Reduction International (HRI) recorded at least 285 executions for drug offences globally during the year, a 118% increase from 2021, and an 850% increase from 2020. Executions for drug offences are confirmed or assumed to have taken place in six countries: Iran, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, plus in China, North Korea and Vietnam – on which exact figures cannot be provided because of extreme opacity. Therefore, this figure is likely to reflect only a percentage of all drug-related executions worldwide. Confirmed death sentences for drug offences were also on the rise; with at least 303 people sentenced to death in 18 countries. This marks a 28% increase from 2021.
These setbacks were not completely unexpected, nor unpredictable. After defending its barbaric policy on the death penalty throughout 2021, Singapore issued execution warrants against individuals convicted of drug trafficking in February 2022. These were eventually stayed after legal appeals and pleas from families and civil society, but more execution warrants quickly followed. In Saudi Arabia, civil society had warned of the risk of resumption in drug-related executions since the partial moratorium was announced in 2021. When the Kingdom carried out the worst mass execution in its history in March 2022, the risk became even more apparent. Similarly, Iranian civil society warned of the risk of a spike in executions, absent persistent international pressure.
This regression was met with robust resistance, as 2022 also featured strong activism from civil society and victims’ families. In Singapore, a wave of protests kicked off – one that has rarely been seen in the country due to extreme limitations on assemblies and routine intimidation of activists. This reaffirmed the key role of civil society in promoting the abolition of the death penalty. The same activism materialised online. Groups such as the Transformative Justice Collective shed light on the vulnerability and marginalisation of those facing execution (thus countering the over-simplistic narrative of the state);7 and launched the ‘Stop the Killings’8 campaign for a moratorium on the use of capital punishment. These initiatives were met with hostility and reprisals by the government. Singaporean human rights defenders were interrogated for potential offences under the Public Order Act 2009 for their advocacy work against the death penalty – a case later dropped;9 while lawyers representing people on death row faced arbitrary disciplinary action and were ordered to pay prohibitive costs for failed applications.10 The Singaporean government also publicly responded to those criticising the resumption in executions, including a UN Special Procedure mandate holder and civil society groups.11
Similar hostility towards human rights defenders was also observed in Bangladesh, where the government cancelled the NGO licence of Odhikar, a prominent NGO already under significant pressure, and virtually the only group monitoring and reporting on the use of capital punishment in the country. While not directly related to the organisation’s anti-death penalty work, this new attack risks further limiting the availability of information on capital punishment in a country where transparency is already lacking.
In Iran, families of people on death row reportedly confronted an increasingly repressive state apparatus by carrying out peaceful protests against the rising number of executions. In response, some were arrested and detained.
In the context of these regressive trends, institutional actors and fellow states have failed to adequately respond. The death penalty for drug offences received some attention in intergovernmental fora throughout 2022 (including within a UN Secretary General’s report to the Human Rights Council).14 Some executions were met with statements of condemnation from various actors, including the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, the European Union, and other diplomatic missions. But, these responses were largely ad-hoc and symbolic, and widely insufficient. In addition, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) – the only UN agency with an explicit mandate on drug-related matters – failed to take any public position on this practice for the second year in a row. The fact that these blatant violations of international standards and official commitments avoided almost all political, diplomatic, or economic repercussions sends a dangerous message to retentionist countries that executions, and therefore death sentences, can continue with impunity.
While more countries abolished the death penalty in 2022, the use of capital punishment for drug offences is going in a markedly different direction, impinging on the likelihood of achieving global abolition. Despite the adoption of a new UN General Assembly Resolution for a moratorium on the use of the death penalty, with historic support from 125 countries (compared to 123 in 2020), known executions for drug offences are back to amounting to over 30% of all global executions – the highest recorded figures since 2017.
These figures are a call to action to all actors involved in the fight for abolition, but primarily to governments and to intergovernmental actors: to acknowledge the barrier that punitive drug policies represent for the global fight towards abolition, and to identify and pursue new, influential strategies to promote the respect of international standards on the death penalty.

Related resources
Don't miss our events and publications
Subscribe to our newsletter